| M | | Mega-. The prefix in the metric system for million. In computerdom, 220
, or 1,048,576.
|
| m | | Milli-. One thousandth. Also sometimes, micro- (millionth). (The lowercase m is used if the more correct Greek letter mu is unavailable for micro.)
|
| MacBench® | | A subsystem-level benchmark from Ziff Davis Labs that measures the processor, floating
point, disk, graphics, video, and CD-ROM performance of a Mac OS system.
|
| macro | | A series of commands and procedures that are carried out in response to a single command or keystroke, or identified by a single name.
|
| magnetic storage | | Disks or tape instead of RAM or optical media to store data.
|
| magneto-optical | | Refers to disks and drives that record data on magnetic tracks, but use optical technology (a laser) to align the read/write head with the tracks. Also refers to disks and drives that directly influence the magnetic signals on the disk with light emitted from lasers.
|
| mailbox | | Term generally relating to how your fax/modem card stores voice mail. One computer can have many mailboxes, each designated for a different purpose or user.
|
| main memory | | The main RAM used by a CPU. The first megabyte of memory in a DOS computer.
|
| mainframe | | A very large, fast, multiuser computer. Usually at least as big as a refrigerator.
|
|
mark
| | In data transmission, setting the parity bit to always be 1. Also called mark parity.
|
| maskable interrupt | | An interrupt that can be interrupted by another interrupt.
|
| mass storage | | Any device used to store large amounts of data. Usually refers to hard disks and tape backup units.
|
| math coprocessor | | A coprocessor that performs floating-point operations for the CPU.
|
|
MB
| | Megabyte. 220
or 1,048,576 bytes. Informally, a million bytes. A unit of memory and data storage size. Two Scientific American magazines total about a megabyte. |
| Mb | | Megabit. 2
20
or 1,048,576 bits. Informally, a million bits.
|
| Mb/s | | Megabits per second. A unit for speed of transfer of data between a hard disk and RAM.
|
| MDRAM | | Multibank Dynamic Random Access Memory. Memory normally used in video boards that boasts extended performance with high bandwidth and short access times. The MDRAM chip can access several memory banks at a time.
|
| media | | Physical materials for storing any kind of information. Media is plural; "medium" is the singular.
|
| meg | | Informal for megabyte. |
| megabyte | | See
MB. |
| megaflops | | See
MFLOPS. |
| memory | | A place in computer circuitry that stores data. See
RAM, ROM, buffer, cache. Also
the tendency in NiCad batteries to retain their charge and lose their ability to be recharged.
|
|
memory chip
| | A chip that stores data. Compare
logic chip.
|
| menu | | A list of choices on a computer screen. Usually the user picks a choice by typing the desired item number or by highlighting the desired item and pressing Enter.
|
| menu bar | | A list of menu headings arranged horizontally, usually at or near the top of the screen. Commonly found in GUIs.
|
|
menu driven
| | Software whose commands are menu choices, frequently arranged hierarchically. Compare
command line
and
GUI
. |
| menu item | | A choice in a menu. |
| mesh topology | | A network topology that has more than one path to each node.
|
|
MFLOPS
| | (megaflops) Million Floating Point
Operations Per Second. Used to measure of the speed of a CPU or computer.
|
| MFM | | Modified Frequency Modulation encoding. A way of recording data on a hard disk. Compare
RLL. |
|
MHz
| | MegaHertz. Millions of cycles per second. The unit of frequency used to measure the clock rate microprocessors. |
| micro | | Literally, one millionth. Also A prefix for almost anything having to do with microcomputers. In measurements, usually abbreviated with m if the character is available.
|
| Micro Channel Architecture | | A 32-bit bus architecture found in some IBM PS/2 computers. See
bus. |
| microcomputer | | A computer small enough to fit on a desktop, with a single-chip CPU.
|
| microelectronics | | Electronic circuits on chips. |
| microfloppy | | A 3.5" floppy disk. |
| microprocessor | | The main logic chip in a microcomputer. The CPU.
|
| MIDI | | Musical Instrument Digital Interface. An interface for connecting suitably equipped musical instruments to suitably equipped computers.
|
| MIF | | Management Information File.
A file stored on a PC that holds system data such as a model ID and serial number that can be manipulated over a network from a
centralized location.
|
| MIME | | Multipurpose Internet Mail
Extensions. A standard for email and Web documents that allows the transfer of multimedia (graphics, audio, etc.).
|
| mini | | Minicomputer. |
| minicomputer | | A computer about the size of a two-drawer filing cabinet, between a micro and mainframe in power.
|
| MIPS | | (mips) Million Instructions Per Second. A measure of processor speed. |
| MIS | | Management Information Services. The department in a company that operates and maintains the company's networked computers.
|
| MMU | | Memory Management Unit. Circuitry that manages the swapping of blocks of memory.
|
| MMX | | Multimedia Extensions. An enhancement in processor architecture that enhanced multimedia and communcations. This technology processes multiple data elements in parallel, speeding up such things as image processing, motion video, speech synthesis, telephony, and 3D graphics.
|
| mobile Triton chip set | | A technology devised by Intel® that allows notebook PCs to approach the same functionality/performance as desktop PCs. The chip set boasts energy-efficient architechture (longer battery life) and streamlines operations, making the notebook PC a more functional part of the computer family.
|
| modem | | Short for modulator-demodulator. A device that enables a computer to communicate with other computers over telephone lines.
|
| monitor | | The part of a computer that looks like a TV. The video display of a computer.
|
| motherboard | | See
system board. |
| mouse | | A hand-held device for moving the cursor or pointer on the screen. Movements of the mouse produce analogous movements of the pointer.
|
|
mouse acceleration
| | The ratio of mouse speed to the distance the pointer travels. Compare
mouse tracking,
mouse sensitivity. |
|
mouse sensitivity
| | The inverse of mouse tracking. Low sensitivity equals fast tracking. The larger the mouse movement for a given pointer distance, the greater the sensitivity.
|
|
mouse tracking
| | The ratio of mouse movement (distance
) to pointer movement. Fast tracking means that a small mouse movement results in a large pointer movement. Compare
mouse acceleration,
mouse sensitivity.
|
| MPC | | Multimedia Personal Computer. A computer capable of performing multimedia functions. Generally defined as at least a 386/16SX system with 2MB RAM, a 30MB HDD, VGA or VGA+ display, a 8-bit sound card, a mouse, and a CD-ROM that uses less than 40% of CPU power. The standard is defined in detail by the MPC Advertising Council.
|
| MPC2 | | Multimedia Personal Computer Level 2. A computer capable of performing multimedia functions. Generally defined as at least a 486/25 system with 4MB RAM, a 160MB HDD, video resolution of at least 640x480 with 65,536 colors, a 16-bit sound card, a two button mouse, and a CD-ROM that uses less than 40% of CPU power. The standard is defined in detail by the MPC Advertising Council.
|
| MPC3 | | Multimedia Personal Computer Level 3. A computer capable of performing multimedia functions above those of an MPC2. Generally defined as at least a Pentium system with 8MB RAM, a 540MB HDD, a sound card, a mouse, and a CD-ROM that uses no more than 40% CPU utilization for a sustained 550 KB/sec transfer rate under Windows 3.11 or DOS and no more than 7% CPU utilization for a sustained 550 KB/sec transfer rate under Windows 95, OS/2, and Windows NT. The standard is defined in detail by the MPC Advertising Council.
|
| MPEG | | Moving Pictures Expert Group. Audio/Video technology that allows for better than VHS quality video and almost CD quality audio by utilizing advanced compression techniques.
|
| MPS | | Multi-Processing System. A computing system employing two or more connected processing units to execute programs simultaneously. See CPU or microprocessor.
|
| MS-DOS | | Microsoft Disk Operating System. A single user operating system for PCs from Microsoft.See
operating system. |
| ms | | Millisecond. A measure of hard disk access time.
|
| MSI | | Medium Scale Integration. A chip that has 10 to 100 components on it.
|
| MTBF | | Mean Time Between Failures. A measure of hardware reliability usually associated with hard drives.
|
| multifunction board | | An expansion card that performs more than one function.
|
| multimedia | | Combining static media (such as text and pictures) with dynamic media (such as sound, video, and animation) on the same system.
|
| multi-session | | A technology relating to CDs (Photo CDs in particular) that allows multiple writes to a single CD. For instance, one can add more pictures to a Photo CD at a later time until the Photo CD is full.
|
| multisynch monitor | | A monitor able to display output within a range of different horizontal and vertical scan frequencies, enabling it to work with a variety of video cards.
|
| multitasking | | The ability of a computer, operating system, or application to perform more than one task or operation at the same time. For example, a multitasking operating system might let you simultaneously use your computer system to download information from a remote computer with a modem, print out a word processing file, and sort a data base.
|
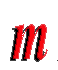 s
s![[Products]](/file/26092/MACD 5.bin/www/firmy/gateway/product_guide.gif)
![[Global Site]](/file/26092/MACD 5.bin/www/firmy/gateway/global_sites.gif)
![[Tech Support]](/file/26092/MACD 5.bin/www/firmy/gateway/tech_support.gif)
![[Corporate Information]](/file/26092/MACD 5.bin/www/firmy/gateway/corp_info.gif)
![[The Cow Zone]](/file/26092/MACD 5.bin/www/firmy/gateway/the_cow_zone.gif)
![[What's New]](/file/26092/MACD 5.bin/www/firmy/gateway/what's_new.gif)
![[Glossary]](/file/26092/MACD 5.bin/www/firmy/gateway/glossary.gif)
![[Search]](/file/26092/MACD 5.bin/www/firmy/gateway/search_engine.gif)
![[Home]](/file/26092/MACD 5.bin/www/firmy/gateway/home.gif)